Tech News
‘Moon to Mars—That’s our outlook’: NASA astronaut Suni Williams on her hopes for the future
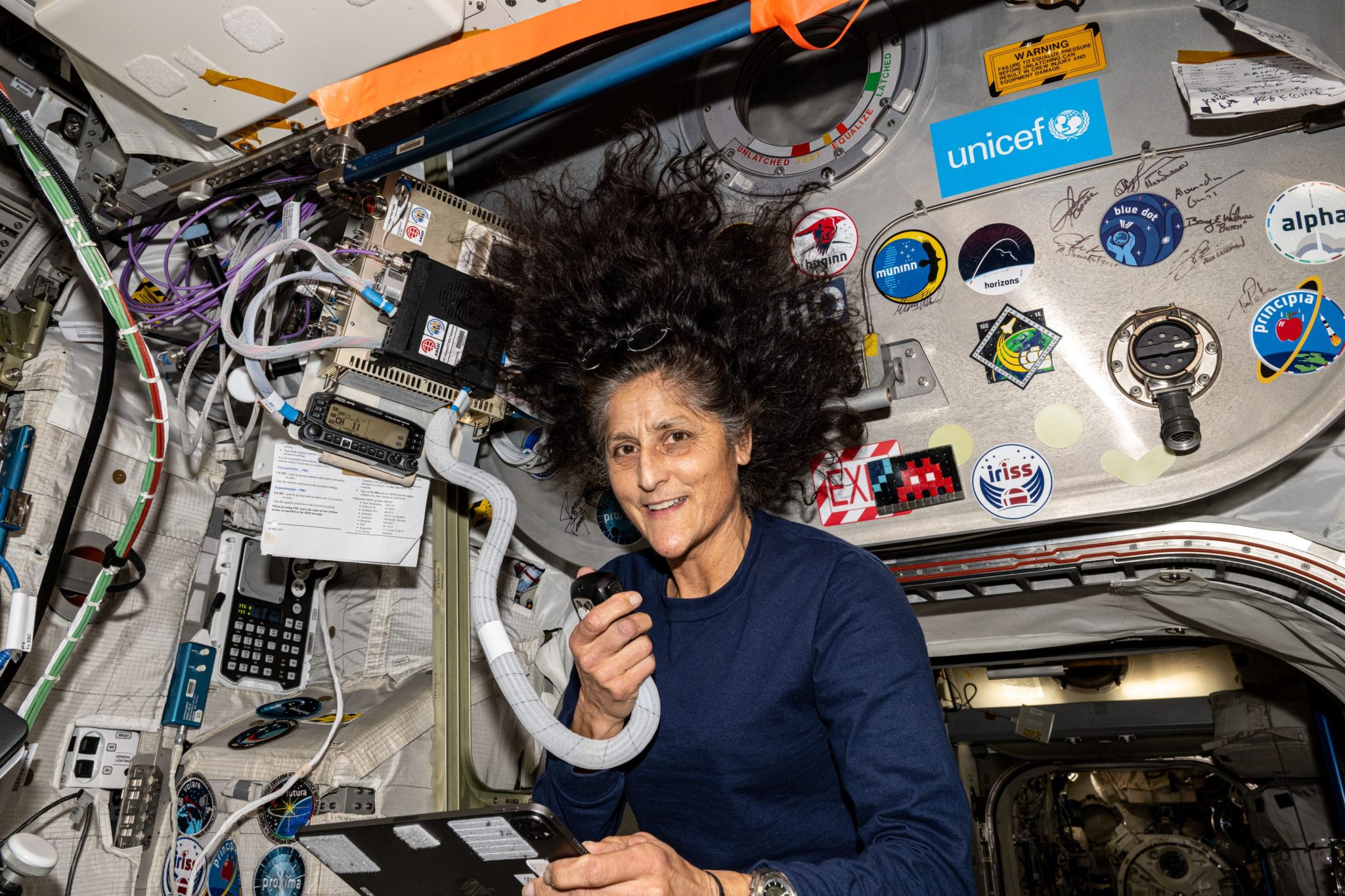

For NASA’s Sunita “Suni” Williams, a scheduled eight-day trip to the International Space Station last summer has instead become a nine-month work assignment.
Williams, 59, and fellow astronaut Butch Wilmore initially remained at the ISS last June after the Boeing Starliner craft they were aboard malfunctioned. Officials ultimately decided to return the Starliner to Earth uncrewed last September, while William and Wilmore, now fully integrated into the crew of Expedition 72 at the ISS, stayed in space.
A veteran of two previous space missions, Williams has served as the station’s commander since September. She and Wilmore are scheduled to return to Earth aboard the SpaceX Dragon as early as Tuesday, March 18, according to NASA. A replacement crew arrived at the space station over the weekend, following a scrubbed launch attempt by NASA and SpaceX last week due to a ground system issue at the launch pad.
By the time of their scheduled landing, Williams and Wilmore’s mission will clock in at nearly 290 days, one of the longer assignments in our history of space travel. Once on terra firma, though, Suni Williams likely will be thinking of space again. And she appears certain of the next move by the U.S. in that regard: a trip back to the future.
“The moon to Mars—that’s our outlook,” Williams says.
In an extensive interview with Fortune months before her mission began, Williams expanded on that idea—and the short- and longer-term outlook for space travel.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Fortune: First of all, why space, and why now?
Suni Williams: It’s just what the human body does—it explores, among other things. We all have curiosity; we’re born with it. Maybe some of that gets pushed down a little bit by society and things going on around us, but we’re all curious and we want to explore. As a nation, this is one of those things that gives people hope and understanding about things that are bigger than themselves.
What is out there that we still want to know about?
I think we want to know where our place in the universe is. When you’re here on Earth, you’re driving around thinking things like, “I’ve got to get to work. I’ve got to get in line at Dunkin’ Donuts or Starbucks.” We’re pretty myopically focused on the here and now. When you go out into space, and you actually see that this is just the little island that we all live on, it becomes more philosophical: What is our purpose here? What happened to our planet, and what is happening to our planet now?
That’s where Mars comes in to play?
If we went there, we might get some insights on what’s going to happen eventually here. How we keep our planet viable, and all of those other questions, may be answered when we just start to think and expand our horizon a little bit more by going to space.
And that starts with going back to the moon?
I don’t know how we’re going to go to Mars, and I don’t think anybody really knows exactly. But in the process of actually trying to get back to the moon sustainably and (then) onto Mars, I’d say we are going to learn something. We’re going to learn a lot about how to do things physically—engineering—but we’re also going to learn about us as human beings and how we tackle problems, and how we face problems in the future with other countries and cultures as we start to leave.
So what does that look like?
The moon to Mars—that’s our outlook. We want to go back to the moon sustainably, which means we need to have a lander presence there. We need to probably have a space station—we’re designing Gateway as a jumping-off point to get to the moon and off the moon, where we do science experiments, where we could build something on the moon sustainably. It seems a little bit like science fiction, a little bit crazy when we think about landers and spacecraft and all that stuff. But when I first got to the NASA building, the International Space Station seemed like it was crazy idea, too. We’ve done that. I don’t put anything past the human mind to be able to do.
When will we have a station on the moon, and then on Mars?
It’s not a quick thing. I think in this decade we will be having people on the moon, and I think the idea would be that as soon as we can get it going, we would want to start having some type of presence on the moon sustainably. As soon as we put people there, we’ll understand how hard it is to do it. Remember, we’re not going to the same place that we did for the Apollo program. It’s a little bit trickier. We’re at the pole, so it’s a different orbit. It’s a different environment.
That will get us ready. Some of the people who are building rockets that might go to some of these places, they are leaving them out in the environment, not necessarily a clean room, so that they can understand what a terrible environment would do to them. People are already thinking about leaving stuff on the moon for a little while and then trying to get it off of the moon. We’re already in the baby steps of understanding how this process is going to work.
Going to the moon would be a common occurrence?
Our idea is to be able to take people regularly to the moon and build our space station there. It’d be the practice ground for how we’re going to then understand how we could take people to Mars…We’ve gotten comfortable with going to low earth orbit (like the ISS). We know how to do it. It’s rockets. It’s dangerous, but we know how to do it. Let’s let companies be able to do that on a regular basis, and we can take the next step of exploration.
Speaking of companies, there’s been explosive growth in the private sector of space travel and production. Does that factor in to all this?
We got a taste of it here at NASA with space tourism, as the Russians were bringing some tourists up to the International Space Station. We embraced it and got on with it, and we started to understand that there’s an avenue here for commercialism. We were then contracting for commercial space supply, and then looking at commercial crew options for the International Space Station. So all of that sort of started to crack open around in the 2000’s, and it has really accelerated in the last decade.
Is there a benefit to the public?
Folks have recognized that this is an interesting way to get things to space, a little bit cheaper for the tax dollar, potentially. But the bigger and better thought is, let’s let these people design the spacecraft the way they want to. Let their creativity guide the way. They could do something and not perhaps be hindered by the way we’ve always done it, because times are changing. So there have been advances in manufacturing processes, 3D printing of metals on a large scale, friction stir welding, other types of processes like that.
And computing power as well?
It’s crazy how much computing power can be in a phone, for example—much more than the computers on the space shuttle. All these types of technological advancements, materials, chemicals, new ideas of using fuels for rocket engines—that’s all sort of been opened up as we’ve opened up to the commercial side. It’s like, let’s let people be creative and try to do this better and smarter. Of course, it’s expensive. The U.S. government has helped some of these companies along the way by rewarding contracts.
What are the main sectors where we might see future growth with regard to space exploration?
Rockets, of course. But also materials, suits, landers. If you’re going to put a human someplace, every aspect of that person going there for a long period of time needs to be adapted. So it’s food, it’s exercise, it’s clothing, some of these little basic things. We have to come up with creative ways to do all of that. Whenever I’m talking to any kids and they’re thinking about what they want to do as a career, I say, ‘You can do anything and be in the space business.’ You do not have to be an astronaut, an engineer or a doctor.
There is still so much we don’t know.
We’ve been able to come back (from space) and be okay. But you want to see how people are going to do when they live in space for a long period of time. The moon’s not that far, but that mission would be a couple of weeks long. They’ll be in microgravity the whole time. As we go further than that—going to Mars is going to be a long trip. Being on Mars is going to be a while, and it’s not going to be Earth gravity. So we have to learn. We have to figure it out.
This story was originally featured on Fortune.com
Tech News
Trying to hire AI talent? A tech CFO says look for acquisitions
Good morning. A big part of ensuring AI investments boost the bottom line is having the right talent.
Companies that use artificial intelligence have continued hiring for AI-related roles over the past 12 months, according to the latest report by McKinsey, “The state of AI: How organizations are rewiring to capture value.” The research examines how companies are redesigning workflows, elevating governance, and mitigating more risks.
Several new risk-related roles are becoming part of organizations’ AI deployment processes. For example, 13% of respondents say their companies have hired AI compliance specialists, and 6% report hiring AI ethics specialists.
The survey is based on 1,491 participants in 101 nations representing a range of industries and functional specialties, according to McKinsey. Forty-two percent of work for organizations with more than $500 million in annual revenues.
Executives at large companies report they’re hiring a broad range of AI-related roles, such as AI data scientists, machine learning engineers, and data engineers. They continue to see these roles as challenging to fill, according to the report.
Another key finding is that AI data scientists will continue to be in high demand in the year ahead. Half of respondents whose organizations use AI say their employers will need more data scientists than they have now.
CFOs are increasingly involved in steering an organization’s AI strategy. “I own AI transformation here,” Alka Tandan, CFO of tech company Gainsight, Inc., which provides a customer success platform, told me. I asked Tandan if Gainsight is seeking to hire AI data scientists.
“We bought an AI company called Staircase and created a separate AI division,” she said. “This division has several data scientists and we plan to add more. We found that buying a company was the easiest way to add bulk to our AI team.”
Akash Palkhiwala, CFO and COO of Qualcomm, recently told me that the company’s consistent M&A strategy has been prioritizing smaller technology acquisitions over the last year and a half to bring in talent and AI technologies which get integrated into the company’s portfolio.
On LinkedIn’s list of the 25 fastest-growing jobs, artificial intelligence engineer has been the top job over the past three years. And tech companies are offering the bulk of those jobs. For example, Apple announced last month plans to hire around 20,000 workers over the next four years who will be focused mostly on R&D, silicon engineering, software development, and AI and machine learning.
McKinsey’s survey also found that many of the executives said their companies have reskilled portions of their workforces as part of their AI deployment over the past year. And in the years ahead plan to undertake more reskilling.
Sheryl Estrada
sheryl.estrada@fortune.com
This story was originally featured on Fortune.com
Tech News
Scott Bessent says he’s not worried about the stock market’s ‘healthy correction,’ insisting the Trump administration is only trying to avoid an even bigger financial crisis

- Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said he was not worried about the stock market, as the S&P 500 faced its first market correction since 2023 last week. Bessent said “corrections are healthy,” adding the Trump administration’s policies, largely seen as driving market uncertainty, are necessary for long-term sustainability.
Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent is not worried about the first stock-market correction since 2023, and he says it’s actually “healthy” to have a downturn now to avoid a crisis later.
The S&P 500, which tracks the broader market, fell into a correction last week by dropping 10% from the all-time-high it set earlier this year. The tech-heavy Nasdaq and Dow Jones also fell on March 13, before all three major indexes closed up on Friday.
Still, Bessent in an interview with NBC’s “Meet the Press” said there were “no guarantees” there won’t be a recession. He said he wasn’t worried about stock-market swings and added a downturn now could be a positive in the long term.
“I’ve been in the investment business for 35 years, and I can tell you that corrections are healthy. They’re normal,” he told NBC. “What’s not healthy is straight up, that you get these euphoric markets. That’s how you get a financial crisis. It would have been much healthier if someone had put the brakes on in ’06, ’07. We wouldn’t have had the problems in ’08.”
Bessent’s comments come as the Trump administration’s policies on tariffs and DOGE efficiencies, including mass layoffs and spending cuts, rattle investor confidence. Since the Fed is unlikely to make major changes to its stance on interest rates at this week’s FOMC meeting, a clear message from the administration could be key to reversing the falling market, according to a note by Goldman Sachs analysts.
“If the Administration were to give a clear message that they were prepared to adjust policy to support the economy or that they would prioritize more growth-friendly parts of their agenda, that could provide more immediate relief,” the analysts wrote.
It’s unclear if the Trump administration is willing to stray from its tariff policy, which has seen it impose a broad 25% tariff on steel and aluminum imports that sparked reciprocal tariffs from countries like Canada. Despite the falling market, though, Trump and his officials like Bessent seem unbothered by the prospect of an extended downturn.
In Trump’s first month in office, spending decreased but it still outweighed revenue, with the federal deficit increasing $307 billion in February, up 3.7% year-over-year. Bessent told NBC that had the U.S. remained at its large spending levels, it would have a guaranteed financial crisis. He added the Trump administration’s recent actions are necessary to prevent a future crisis.
“We are resetting, and we are putting things on a sustainable path,” he told NBC.
Despite the recent market setback, analysts at Evercore still see the S&P 500 skyrocketing to 6,800 from its current 5,690 by the end of 2025. Yet, in the worst case, slowing GDP growth of 1.5% and core inflation above 3% may bring on a period of stagflation that could see the S&P 500 collapse to 5,200—even lower than the 5,700 level it recorded when Trump was elected in November.
“A material move below 5,700 without reprieve from Washington signals Trump is less concerned with stocks, more concerned with Radical Change regardless of the asset market fallout,” the Evercore analysts wrote.
For now, Bessent shook off any fears of a long-term shock to markets and said he believed the Trump administration would win over Americans with its policies.
“I’m not worried about the markets. Over the long term, if we put good tax policy in place, deregulation and energy security, the markets will do great,” Bessent said. “I say that one week does not the market make.”
This story was originally featured on Fortune.com
Tech News
Intel’s new CEO stands to reap more than $400 million—but he’ll have to triple the stock price and personally spend $25 million to get it

- Taking a page from the private equity playbook, Intel is requiring its new CEO to put some skin in the game. Lip-Bu Tan has agreed to buy $25 million worth of Intel stock with his own money. And here’s the rub: he won’t get paid if he cashes in. However, if he smashes the lights out with his performance, his pay package has a potential value—which assumes hitting every possible goal at the highest level—of more than $400 million, according to an analysis conducted by Farient Advisors. And for shareholders, that would mean Intel’s market cap grew by $208 billion to a whopping $312 billion.
Intel CEO Lip-Bu Tan had his first day on the job on Monday, and the challenge the chip industry veteran faces is staggering.
The stock, priced around $26, has lost more than half its value since December 2023—although it rallied more than 10% after his appointment—and the company is at a strategic crossroads with its chip design and manufacturing businesses. Tan’s own letter to Intel employees noted it had been a “tough few years” and that the company was at “one of the most pivotal moments in its history.”
But if Tan, 65, can hammer home the strategy and execute what could be a colossal turnaround, the Malaysian-born, Singapore-raised executive could realize a significant pay package based on the terms of the deal he struck with the Intel board, dated March 10. And as for Intel’s shareholders, Tan’s achievement would mean the market cap swelled to more than $300 billion—a level the tech giant hasn’t seen in two decades.
Farient Advisors CEO Robin Ferracone told Fortune that Tan’s remit isn’t limited to executing a turnaround; he very nearly needs to rebuild the company. “Doubling the stock price gets you to where you were a few years ago, but tripling it to the $70 range—Intel hasn’t seen that since about 2000,” said Ferracone. “So, it’s a big lift.”
Tan’s offer letter outlines a complex series of incredibly sky-high hurdles he’ll have to clear flawlessly for shareholders and the company. But he could ultimately wind up with a pay package valued above $400 million if he maxes out all his performance and his potential awards, according to Farient’s analysis of his pay plan. In addition, Tan will have to personally invest $25 million of his own money in the stock during his first 30 days on the job, and hold it for the next five years, meaning he could potentially lose money if he isn’t up to scratch.
“It’s a high-stakes package that reflects both the board’s confidence in his ability to drive a turnaround and a strong commitment to pay-for-performance principles,” corporate strategy consultant Arjan Singh told Fortune.
Tying stock price growth to performance targets sets a high bar, said Singh, managing partner of Corporate War Games and an adjunct professor of marketing and global strategy at Southern Methodist University’s Cox School of Business.
“This signals that the board is aligning executive incentives directly with shareholder returns,” he said. “It also helps mitigate concerns about excessive CEO pay without results—there’s no free equity here, and failure to deliver won’t be rewarded.”
Eric Hoffmann, vice president and chief data officer at Farient Advisors, told Fortune he “can’t stress enough that (Tan’s) grants could fail to vest entirely without stock price appreciation and slightly better than median total shareholder return against the S&P 500.”
Anatomy of a turnaround comp plan
According to Farient’s analysis, Tan’s annual cash pay consists of a base salary of $1 million with a target bonus of $2 million. His annual 2026 go-forward equity grant is valued at $24 million, but he won’t get it until next year.
For the sign-on portion of his deal, Intel gave Tan a new-hire performance stock unit (PSU) grant valued at $17 million and a stock option grant valued at $25 million. But Tan will have to double the stock price to earn the target number of PSUs—plus the stock price must outperform the S&P 500. If Tan succeeds in tripling the stock price, he’ll earn three times the number of shares. In that scenario, the PSU grant would be valued at $153 million, according to Farient’s analysis. The options vest in five tranches over five years. In the tripled-stock-price scenario, the first two tranches of his stock options could be exercised for $39 million and the other three tranches could be exercised for $88 million for a total of $127 million, according to Farient.
For his annual awards, Intel gave Tan a second PSU grant valued at $14.4 million that could be worth $86 million if the stock price triples and Intel hits the shareholder return and stock-price goals for maximum share payout. He also got another grant of stock options valued at $9.6 million which could be exercised at a value of $42 million.
Combining both the sign-on and fiscal 2025 awards, assuming maximum performance and a tripling of the stock price, Tan’s offer has a potential value of some $408 million, according to Farient.
Hoffmann described the compensation scheme as “highly leveraged.” There’s a significant downside for Tan, because he could lose out on his grants, and he could also lose money on his investment, he said.
But if Tan achieves the maximum possible performance, Intel shareholders “will be dancing in the streets,” Ferracone told Fortune, given that Tan’s long-term incentives are “highly aligned with shareholder interests with a recognition that Intel needs to create significant value and catch up if not leapfrog competitors in the AI space.”
The grant date value of his total pay package is $69 million, which includes his salary, target bonus, and value of the options, equity and PSUs, but does not account for realizing the maximum amounts, which could be higher if the stock price rises.
Based on the terms of the offer, that’s exactly what Intel is expecting of Tan—plus much more. The lion’s share of Tan’s potential pay is at risk and equity-based and one of the main components is the new-hire performance stock grant.
“CEO equity awards are often tied to achieving specific operational or financial metrics, but it’s infrequent to require such steep stock price increases,” corporate governance expert and Georgetown University associate professor Jason Schloetzer told Fortune. “In my view, the plan distinguishes itself for its rather aggressive performance criteria.”
Schloetzer noted that CEO compensation plans often have three-year vesting schedules, and Intel’s five-year plan is longer than usual. He said it could reflect the Intel board’s desire “to balance the aggressive target with not motivating excessive risk taking or cutting corners that create long-term harm.”
In a statement, Intel said Tan’s pay package is competitive with the market.
“Lip-Bu’s compensation reflects his experience and credentials as an accomplished technology leader with deep industry experience and is market competitive,” Intel said. “The vast majority of his compensation is equity-based and tied to long-term shareholder value creation.”
Intel’s comp plan design is a clear signal to investors that the company believes in Tan’s ability to reverse the tech giant’s performance, but that he won’t get a free lunch, said Singh. Plus, Tan will be on equal footing with investors at the outset with his vow to buy stock worth $25 million—and then hold onto it for the full five-year period for all his PSUs to vest.
“Obviously, the use of equity-based vehicles, the longer-term vesting of five years, the performance parameters in the plans, and Lip-Bu’s required investment clearly communicates that Lip-Bu’s Job #1 is to create shareholder value, which is totally aligned with shareholders’ interests,” said Ferracone.
As for his personal investment, it’s not a common feature in CEO offer letters, said Courtney Yu, director of research at compensation and governance firm Equilar, and the size of the investment itself is on the higher side relative to CEOs with a similar ask.
Private equity firm CEOs often hold large stakes in the companies they lead, but public company CEOs are typically required to build up an ownership stake over time by holding the equity they get as compensation and maintaining a minimum stake valued at five or six times their annual pay.
“For a public company, this level of financial commitment is a strong signal of personal accountability,” noted Singh. “It ensures the CEO has real skin in the game, which could resonate well with shareholders looking for leadership that is fully committed to Intel’s long-term success.”
Regarding Tan’s $25 million stock purchase, Intel said it “reflects his belief in Intel and commitment to creating shareholder value.”
In addition to the agreement with Tan, Intel announced that it would compensate interim co-CEOs Michelle Johnston Holthaus and David Zinsner with $1.5 million in cash apiece for holding down the fort during the search process after the end of former CEO Pat Gelsinger’s tenure at the chip giant in December.
Similarly, the board’s interim executive chair, Frank Yeary, will return to being Intel’s independent chair. For his time in the interim role, Yeary will get restricted stock units valued at $700,000, the company said.
This story was originally featured on Fortune.com
-

 Tech News3 months ago
Tech News3 months agoHow Costco’s formula for reaching uncertain consumers is pushing shares past $1,000 to all-time highs
-

 Tech News3 months ago
Tech News3 months agoLuigi Mangione hires top lawyer—whose husband is representing Sean ‘Diddy’ Combs
-

 Tech News3 months ago
Tech News3 months agoLego bricks have won over adults, growing its $10 billion toy market foothold—and there’s more to come
-
Tech News3 months ago
Quentin Tarantino thinks movies are still better than TV shows like Yellowstone
-

 Tech News3 months ago
Tech News3 months agoInside the FOMC: Boston Fed President Susan Collins on changing her mind, teamwork, and the alchemy behind the base rate
-

 Tech News3 months ago
Tech News3 months agoNancy Pelosi has hip replacement surgery at a US military hospital in Germany after falling at Battle of the Bulge ceremony
-

 Tech News3 months ago
Tech News3 months agoTrump and members of Congress want drones shot down while more are spotted near military facilities
-

 Tech News3 months ago
Tech News3 months agoHundreds of OpenAI’s current and ex-employees are about to get a huge payday by cashing out up to $10 million each in a private stock sale